In today’s hyperconnected enterprise environment, a robust wireless network infrastructure has become the backbone of business operations. From supporting hundreds of concurrent device connections to enabling seamless video surveillance integration, enterprise-grade access points (APs) must deliver unwavering performance, comprehensive coverage, and military-grade security. The challenge for IT teams and system integrators is designing wireless networks that not only meet current demands but scale efficiently as organizational needs evolve.
This comprehensive guide explores the critical best practices for designing enterprise-grade wireless networks, with a focus on integrating advanced IP camera systems and network video recorders into your wireless infrastructure. Whether you’re deploying surveillance solutions across multiple facilities or upgrading existing network architecture, understanding these principles will ensure optimal performance and future-proof scalability.

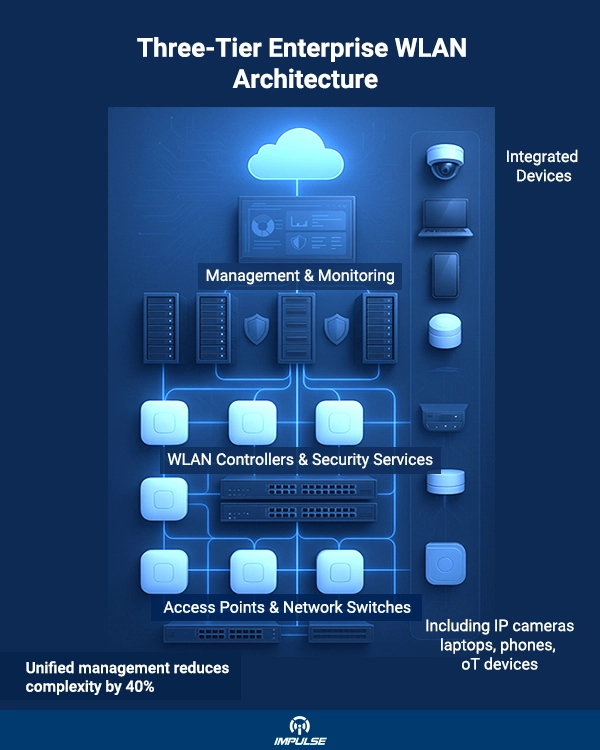
Understanding Enterprise Wireless Network Architecture
Enterprise wireless networks differ fundamentally from consumer-grade solutions. They’re engineered to handle massive concurrent connections often hundreds or thousands of devices including laptops, smartphones, tablets, IP phones, IoT sensors, and increasingly, high-bandwidth devices like IP surveillance cameras.
The architecture typically consists of three critical tiers:
Management Layer: Centralized platform for configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting across all network components
Network Services Layer: Wireless LAN (WLAN) controllers that manage security protocols, RF optimization, and threat detection
Access Layer: Enterprise-grade APs and network switches that provide physical connectivity
For organizations deploying comprehensive security solutions, integrating high-resolution IP cameras such as the 5MP Varifocal Network Bullet camera with adjustable 2.7mm to 13.5mm lens and 50-meter IR capabilities requires careful consideration of bandwidth requirements, network segmentation, and AP placement strategies to ensure uninterrupted high-definition video streaming with quad stream support.
Best Practice #1: Conduct Comprehensive Site Surveys
The foundation of any successful wireless network deployment begins with meticulous site assessment. A wireless site survey involves physically inspecting deployment locations to evaluate environmental factors that impact RF signal propagation.
Key Survey Components:
Physical Infrastructure Assessment: Document building layouts, construction materials (concrete, metal, glass), ceiling heights, and existing cable pathways
RF Environment Analysis: Identify sources of interference including microwave ovens, industrial equipment, neighboring wireless networks, and metal structures
Coverage Mapping: Determine optimal access point placement to eliminate dead zones while avoiding signal overlap that causes co-channel interference
Capacity Planning: Calculate expected device density per area to determine appropriate AP deployment density
For surveillance-heavy environments where advanced PTZ solutions like the 5MP PTZ IP Network camera featuring 40X optical zoom with 4.25mm to 170mm focal lengths and 200-meter IR range require consistent high-bandwidth connectivity for auto-tracking, preset tours, and line scanning, survey data becomes critical for ensuring reliable 24/7 video transmission.
Industry best practices recommend AP densities between 110-185 square meters per access point for optimal 5GHz and 6GHz coverage in standard enterprise environments with 2.4-3.7 meter ceiling heights. This translates to AP spacing of approximately 12-15 meters apart, following a honeycomb pattern where feasible.
Best Practice #2: Implement Role-Based Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is essential for enterprise wireless deployments, especially when integrating surveillance systems with corporate networks. Segregating traffic types enhances both security and performance optimization.

Segmentation Strategy:
Employee Network: Primary corporate SSID with WPA3 encryption for staff devices and business-critical applications
Guest Network: Isolated VLAN with internet-only access, preventing access to internal resources
IoT/Surveillance Network: Dedicated VLAN for IP cameras, access control systems, and building automation devices
Management Network: Separate administrative VLAN for network infrastructure configuration
When deploying enterprise-scale recording infrastructure like the 256-Channel Network Video Recorder with 16 SATA drives delivering 1824 Mbps recording bandwidth and 4K resolution for preview and playback, placing surveillance traffic on isolated VLANs prevents massive video streams from impacting business-critical applications.
Best Practice #3: Optimize RF Design and Channel Planning
Proper radio frequency (RF) design directly impacts network performance, especially for bandwidth-intensive surveillance applications. Modern Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Wi-Fi 6E standards offer significant improvements in channel capacity, but only when configured optimally.
RF Optimization Strategies:
Channel Width Selection: For high-density environments, configure 40MHz channels on 5GHz bands and 80MHz channels on 6GHz bands (where regulations permit) to balance throughput and interference mitigation
Minimum Bitrate Configuration: Set appropriate minimum connection speeds (typically 12-24 Mbps) to prevent legacy devices from degrading overall network performance
Power Level Management: Configure transmit power to ensure adequate coverage without creating excessive co-channel interference between adjacent APs
RX-SOP Tuning: Set Receiver Start of Packet detection at -78 dBm to reduce cell size and minimize interference in dense AP deployments
For applications requiring fixed-position surveillance deploying solutions like the 5MP Fixed Network Dome camera with built-in microphone, 3.6mm fixed lens, and 60-meter IR capability consistent signal strength throughout the coverage area ensures uninterrupted audio-video transmission without packet loss or buffering.
Best Practice #4: Deploy Enterprise-Grade Hardware
The backbone of any robust wireless network is the quality of its access point hardware. Enterprise-grade APs incorporate advanced technologies absent in consumer equipment:
Critical Enterprise AP Features:
MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output): Enables simultaneous communication with multiple client devices, dramatically improving network efficiency in high-density environments
Beamforming Technology: Focuses wireless signals toward connected devices rather than broadcasting omnidirectionally, improving signal strength and reducing interference
Advanced Antenna Arrays: Multiple spatial streams support higher throughput and better coverage patterns
Power over Ethernet Plus (PoE+): IEEE 802.3at or 802.3bt support eliminates separate power infrastructure requirements
Environmental Hardening: Weather-resistant enclosures and extended temperature ratings for outdoor or industrial deployments
High-performance surveillance systems demand enterprise-grade reliability. When managing multiple high-resolution camera streams particularly with advanced edge analytics like motion detection found in cameras such as the 5MP Varifocal Network Bullet camera with audio/alarm I/O capabilities choosing APs with sufficient processing power and backhaul capacity prevents bottlenecks.
Best Practice #5: Implement Converged Network Management
Managing wireless and wired networks separately creates operational complexity and increases the likelihood of configuration errors. Unified network management platforms consolidate control planes into single administrative interfaces.
Benefits of Convergence:
Simplified Operations: Configure both wired and wireless infrastructure from unified dashboards
Consistent Policy Enforcement: Apply security policies, QoS settings, and access controls uniformly across network types
Holistic Visibility: Monitor performance metrics, troubleshoot issues, and analyze traffic patterns across entire infrastructure
Streamlined Upgrades: Deploy firmware updates and configuration changes to all devices simultaneously
For enterprises deploying comprehensive surveillance architectures with high-channel-count NVRs managing hundreds of camera streams at 4K resolution, unified management ensures surveillance network performance doesn’t degrade business operations on shared infrastructure.
Best Practice #6: Leverage AI-Powered Network Intelligence
Modern enterprise wireless solutions increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning for proactive network management. AI-driven platforms offer transformative capabilities:
AI Network Benefits:
Predictive Analytics: Identify potential issues before they impact users through pattern recognition and anomaly detection
Automated Optimization: Dynamically adjust channel assignments, power levels, and load balancing based on real-time RF conditions
Root Cause Analysis: Accelerate troubleshooting by automatically correlating events and identifying underlying problems
Capacity Planning: Forecast future bandwidth requirements and optimal AP expansion locations using historical usage data
When managing surveillance networks with devices featuring edge analytics capabilities such as cameras with built-in motion detection and video analytics AI-powered network management ensures wireless infrastructure keeps pace with increasing computational demands at the network edge.
Best Practice #7: Ensure Scalability and Future-Proofing
Enterprise network design must accommodate growth without requiring complete infrastructure overhauls. Building scalability into initial deployments saves substantial costs and operational disruption.
Scalability Strategies:
Modular Hardware Selection: Choose AP models and WLAN controllers that support incremental expansion without capacity limits
Standards Compliance: Invest in equipment supporting latest Wi-Fi standards (Wi-Fi 6E, upcoming Wi-Fi 7) even if not immediately utilized
Structured Cabling: Deploy Category 6A or higher cabling to support multi-gigabit speeds and Power over Ethernet requirements
Cloud Management Options: Consider cloud-managed solutions that eliminate on-premises controller constraints and enable unlimited scalability
Organizations planning to expand video surveillance coverage adding more bullet cameras, dome cameras, or PTZ units to existing NVR infrastructure benefit from wireless networks designed with 20-30% capacity headroom beyond current requirements.
Best Practice #8: Prioritize Comprehensive Security
Wireless network security demands multiple defense layers, particularly for enterprises transmitting sensitive data or surveillance video across Wi-Fi infrastructure.
Security Best Practices:
WPA3 Enterprise Encryption: Deploy the latest wireless security protocol with 192-bit security mode for maximum protection
Certificate-Based Authentication: Implement 802.1X with RADIUS servers for device and user authentication
Network Access Control (NAC): Enforce device posture checks before granting network access
Regular Firmware Updates: Maintain current software versions on all APs, controllers, and network equipment to patch vulnerabilities
IDS/IPS Integration: Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems to identify and block malicious wireless activity
Rogue AP Detection: Continuously scan for unauthorized access points that could compromise network security
For surveillance systems transmitting high-value security footage, implementing robust wireless security prevents unauthorized access to camera feeds while ensuring video integrity throughout transmission to network video recorders.
Best Practice #9: Establish Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
Deploying enterprise wireless infrastructure is just the beginning ongoing network monitoring and proactive maintenance ensure sustained performance.
Monitoring Framework:
Performance Metrics: Track throughput, latency, packet loss, retry rates, and connection success rates across all APs
RF Environment: Monitor for new interference sources, neighboring network changes, and channel utilization
Device Health: Track AP uptime, hardware temperature, PoE power consumption, and error logs
Client Experience: Measure connection quality, roaming performance, and application-specific metrics
Capacity Utilization: Analyze bandwidth consumption patterns and identify areas approaching saturation
Organizations operating 24/7 surveillance systems with continuous video recording to high-capacity NVRs particularly benefit from proactive monitoring that prevents recording gaps due to wireless connectivity issues.
Best Practice #10: Optimize for Surveillance Workloads
IP camera integration introduces unique wireless network considerations that differ from typical enterprise applications:
Surveillance-Specific Optimizations:
Bandwidth Reservation: Allocate dedicated bandwidth for surveillance traffic using QoS policies that prioritize video streams
Multicast Configuration: Configure efficient multicast routing for scenarios where multiple viewers access live camera feeds
Jitter Minimization: Implement traffic shaping and buffering strategies to ensure smooth video playback without artifacts
Redundancy Planning: Design AP coverage with overlapping cells so roaming cameras maintain connectivity without interruption
When deploying advanced surveillance solutions featuring varifocal lenses, PTZ functionality, and high-resolution sensors, the wireless infrastructure must support consistent multi-megabit streams per camera without introducing latency that impacts real-time monitoring or forensic review.
Conclusion
Designing robust enterprise-grade wireless networks requires strategic planning, quality hardware selection, and adherence to proven best practices. From comprehensive site surveys establishing optimal AP placement to implementing AI-powered management platforms that predict issues before they impact operations, each element contributes to a wireless infrastructure capable of supporting demanding applications.
For organizations integrating advanced IP surveillance systems across their wireless infrastructure, the network becomes mission-critical infrastructure that must handle everything from fixed monitoring to dynamic PTZ operations and high-capacity recording. Following these ten best practices ensures your wireless deployment delivers the performance, security, scalability, and reliability modern enterprises demand.
By investing in proper wireless network design today, organizations position themselves to seamlessly adopt emerging technologies tomorrow, from 4K and 8K surveillance to AI-powered video analytics operating at the network edge.
Partner with Impulse to design and deploy surveillance-grade wireless networks that deliver uncompromising performance. Whether you’re planning a new installation or upgrading existing infrastructure, we supply comprehensive surveillance solutions and high-performance equipment that integrate seamlessly into your wireless architecture.


