The landscape of secure access control has undergone a remarkable transformation in 2025. Traditional password-based systems and physical keys are rapidly becoming obsolete as organizations embrace biometric authentication technology for enhanced security and seamless user experiences. With fingerprint recognition, facial recognition systems, and iris scanning technology at the forefront, biometric solutions are redefining how we protect sensitive areas, data, and infrastructure.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the technical evolution of biometric access control, examine the three dominant recognition technologies, and understand how modern systems like advanced TCP/IP access control boards are revolutionizing security infrastructure for businesses, government facilities, and high-security environments.

Understanding Biometric Authentication: The Foundation of Modern Security
Biometric authentication leverages unique physiological or behavioral characteristics such as fingerprints, facial structures, and iris patterns to verify individual identity. Unlike traditional security methods that rely on something you know (passwords) or something you have (access cards), biometrics focuses on something you are, making it inherently more secure and difficult to replicate.
The Three Pillars of Biometric Recognition in 2025
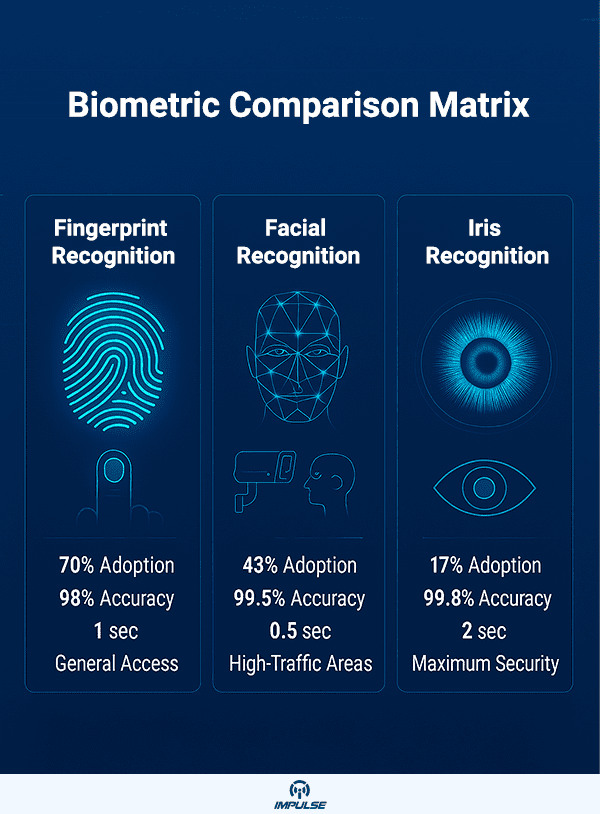
1. Fingerprint Recognition: The Most Widely Adopted Technology
Fingerprint biometrics continues to dominate the access control landscape with an impressive 70% global adoption rate. The technology has evolved significantly from traditional optical scanners to advanced ultrasonic fingerprint sensors that can detect accurate readings even with wet or dirty fingers, improving detection accuracy by approximately 30% compared to earlier generations.
Modern fingerprint systems utilize sophisticated algorithms that analyze minutiae points the unique ridge endings and bifurcations on fingertips converting them into encrypted digital templates. These templates are stored securely and compared during authentication attempts, providing verification accuracy rates of 98% or higher in optimal conditions.
Technical Advantages:
- False Acceptance Rate (FAR): Less than 0.001%
- Processing Speed: Authentication in under 1 second
- Template Size: 256-1000 bytes (minimal storage requirements)
- Durability: Fingerprints remain stable throughout a person’s lifetime
For organizations implementing two-door access control systems or four-door access control boards, fingerprint technology offers an excellent balance of security, speed, and cost-effectiveness. When integrated with advanced access control boards like the TCP/IP Two Doors Access Control System or the TCP/IP Four Doors Access Control System, fingerprint readers can manage multiple entry points with features including multi-computer management, regional interlocking, and fire linkage capabilities.
2. Facial Recognition Systems: The Contactless Revolution
Facial recognition technology has witnessed explosive growth in 2025, with 43% of consumers now using this biometric method regularly. The shift toward contactless biometrics accelerated dramatically, driven by hygiene concerns and the demand for faster, friction-free authentication experiences.
Modern facial biometric systems employ sophisticated AI-powered algorithms that analyze up to 80 nodal points on a human face, including the distance between eyes, nose width, cheekbone shape, and jaw line contour. These measurements create a unique facial signature or template that can be matched in real-time, even in challenging conditions such as varying lighting, partial occlusions, or different facial angles.
Technical Specifications:
- 3D Facial Recognition Accuracy: 99.5%+ in controlled environments
- Recognition Speed: 0.3-1.5 seconds per face
- Detection Distance: 0.5 to 5 meters depending on camera resolution
- Presentation Attack Detection (PAD): Advanced liveness detection prevents spoofing attempts using photos or videos
The integration of AI and machine learning in facial recognition has led to continuous system refinement, enabling these solutions to defend against sophisticated threats including deepfakes. Systems now incorporate micro-expression analysis and behavioral pattern recognition to distinguish between genuine individuals and fraudulent attempts.
For facilities requiring high-throughput access control such as corporate campuses, hospitals, or educational institutions facial recognition paired with advanced components like QR Code Card Readers provides a powerful dual-authentication approach. These readers feature advanced RFID circuitry and image recognition capabilities, supporting QR codes, MIFARE, NFC, and other card types with high sensitivity and low power consumption.

3. Iris Scanning Technology: Maximum Security Applications
Iris recognition represents the pinnacle of biometric security technology, offering unparalleled accuracy and resistance to fraud. While currently at 17% adoption globally, iris scanning is gaining significant traction in high-security applications including healthcare facilities, financial institutions, government agencies, and critical infrastructure protection.
The iris the colored ring surrounding the pupil contains a complex pattern of furrows, ridges, crypts, and pigmentation spots that remain stable from infancy through death. Iris scanning systems use near-infrared light to illuminate the eye and capture high-resolution images, which are then processed to extract the unique iris pattern and create a biometric template.
Technical Performance Metrics:
- False Rejection Rate (FRR): Approximately 1 in 1.2 million
- Uniqueness: 266 distinctive characteristics vs. 40-60 for fingerprints
- Scan Time: 1-2 seconds for bilateral iris capture
- Working Distance: 10-40 cm depending on system configuration
- Spoofing Resistance: 99.8% with live detection algorithms
Iris recognition excels in environments where maximum security is paramount and where contactless, hygienic authentication is essential. The technology works effectively regardless of external factors like dirty hands or facial coverings, making it ideal for sterile environments.
Multimodal Biometric Systems: The Future of Access Control
The evolution toward multimodal biometric authentication represents one of the most significant trends in 2025. By combining multiple biometric modalities such as fingerprint and facial recognition or facial and iris scanning organizations can achieve unprecedented security levels while maintaining user convenience.
Multimodal systems provide 96% higher security compared to single-factor authentication methods. This approach addresses the limitations of individual biometric technologies:
- Redundancy: If one biometric fails (dirty fingerprint, poor lighting for facial recognition), the system can authenticate using an alternative method
- Enhanced Anti-Spoofing: Multiple verification layers make it exponentially more difficult for attackers to breach security
- Improved Accuracy: Cross-verification reduces false acceptance and rejection rates
- Flexibility: Users can select their preferred authentication method based on context
Modern access control boards support seamless integration of multiple biometric readers and authentication methods. Advanced systems like the TCP/IP Four Doors Access Control System offer multi-computer management, regional interlocking capabilities, and cloud platform integration, enabling administrators to configure sophisticated multimodal authentication protocols across extensive facility networks.
Technical Infrastructure: Building a Robust Biometric Access Control Ecosystem
Implementing effective biometric access control requires more than just biometric readers it demands a comprehensive infrastructure that ensures reliability, scalability, and security.
Core Components of Enterprise Biometric Systems
1. Biometric Capture Devices
High-quality capture devices form the foundation of any biometric system. Whether deploying MIFARE 13.56MHz IC cards for secure contactless data transmission or advanced card readers, device selection directly impacts system performance. Modern MIFARE cards offer encrypted initialization, long-term data retention, unique serial numbers, and multi-application support with hierarchical key structures and anti-replay protection.
2. Processing and Matching Engines
Sophisticated algorithms convert raw biometric data into encrypted templates and perform real-time matching against enrolled databases. Modern systems leverage AI-accelerated processing to handle thousands of authentication requests simultaneously while maintaining sub-second response times.
3. Network Infrastructure
TCP/IP-based access control systems provide the scalability and flexibility required for enterprise deployments. Unlike legacy systems, TCP/IP architecture enables centralized management, real-time monitoring, remote configuration, and seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure.
4. Physical Access Points
Securing entry and exit points requires reliable hardware including electronic locks, door strikes, and control panels. High-quality components like the Switch Panel Door Exit Push Button, constructed from durable stainless steel, ensure long-term operational reliability in high-traffic environments.
Advanced Features Revolutionizing Access Control in 2025
Dynamic Authentication and Cloud Integration
Modern access control systems have evolved far beyond simple credential verification. Advanced features now include:
Dynamic 2D Code Authentication: Temporally-limited QR codes that change periodically, preventing unauthorized duplication or sharing of access credentials. This technology is particularly effective when combined with biometric pre-authentication for ultra-secure environments.
Cloud Platform Integration: Cloud-connected systems enable remote management, real-time access log analysis, predictive maintenance alerts, and instant credential updates across multiple locations. Administrators can grant or revoke access privileges immediately, regardless of physical location.
Regional Interlocking: Sophisticated access logic that prevents simultaneous access to connected zones, essential for securing sensitive areas where segregation of duties must be maintained. When one door opens in a protected zone, adjacent entry points remain secured until the first door closes and re-secures.
Fire Linkage Systems: Life safety integration that automatically releases secured doors during emergency events, ensuring rapid evacuation while maintaining comprehensive audit trails for post-incident analysis.
Behavioral Biometrics: The Emerging Fourth Pillar
While not yet mainstream, behavioral biometrics is gaining momentum as a complementary authentication layer. This technology analyzes unique behavioral patterns including:
- Gait analysis: Individual walking patterns and movement characteristics
- Typing dynamics: Keyboard rhythm, pressure patterns, and timing between keystrokes
- Signature dynamics: Pen pressure, stroke velocity, and signing rhythm
The primary advantage of behavioral biometrics is continuous authentication rather than verifying identity at a single access point, the system continuously monitors user behavior, detecting anomalies that might indicate credential compromise or impersonation.
Implementation Considerations and Best Practices
Security and Privacy Compliance
Organizations implementing biometric authentication must navigate complex regulatory landscapes. Data protection regulations including GDPR, CCPA, and various state-level privacy laws impose strict requirements on biometric data collection, storage, and processing.
Best Practices:
- Data Encryption: Biometric templates must be encrypted both in transit and at rest using AES-256 or stronger encryption standards
- Template Protection: Store only encrypted templates, never raw biometric images
- Access Logging: Maintain comprehensive audit trails of all authentication attempts and administrative actions
- Consent Management: Obtain explicit consent before collecting biometric data and provide clear opt-out mechanisms
- Data Minimization: Collect only the biometric data necessary for authentication purposes
System Reliability and Redundancy
Mission-critical access control systems require robust failover mechanisms:
- Backup Power Systems: Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and battery backup ensure continued operation during power outages
- Redundant Controllers: Duplicate control hardware prevents single points of failure
- Local Authentication Databases: Distributed credential storage enables continued operation even if network connectivity is lost
- Manual Override Mechanisms: Physical key overrides provide emergency access when electronic systems fail
Future Trends: What’s Next for Biometric Access Control
AI-Powered Predictive Security
Machine learning algorithms are enabling predictive security capabilities that go beyond simple authentication. Systems now analyze access patterns to detect anomalies, predict potential security incidents, and automatically adjust security postures based on threat intelligence.
Applications include:
- Detecting unusual access patterns that might indicate credential compromise
- Identifying potential insider threats through behavioral analysis
- Automatically escalating authentication requirements during heightened threat periods
- Correlating access events across multiple systems to detect coordinated attacks
Biometric-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Cloud-based BaaS platforms are democratizing access to enterprise-grade biometric security, particularly benefiting small and medium-sized enterprises. These platforms offer:
- Subscription-based pricing models with minimal upfront investment
- Automatic software updates and feature enhancements
- Simplified deployment and management
- Scalability from single-door to multi-site deployments
Edge Computing and Local Processing
Privacy concerns and latency requirements are driving the adoption of edge computing in biometric systems. Rather than transmitting biometric data to centralized servers, edge-enabled devices like advanced ID Card Writers featuring fast reading speeds and high-quality microcomputer control with USB compatibility process authentication locally, reducing exposure of sensitive data while improving response times.
Conclusion
As we navigate through 2025, biometric authentication technology has firmly established itself as the cornerstone of modern secure access control. The convergence of fingerprint recognition, facial recognition systems, and iris scanning technology with advanced infrastructure components creates comprehensive security ecosystems that balance protection with user convenience.
Organizations investing in modern access control systems from TCP/IP multi-door controllers to sophisticated card readers and biometric sensors position themselves at the forefront of security innovation. The integration of AI, cloud platforms, and multimodal authentication creates robust defenses against evolving threats while delivering the seamless experiences users expect.
The future of access control is not just secure it’s intelligent, adaptive, and inherently human-centric. By understanding the technical capabilities and implementation considerations of biometric technologies, security professionals can design systems that protect assets, streamline operations, and build trust in an increasingly digital world.
Don’t let outdated security infrastructure put your organization at risk. Impulse offers cutting-edge biometric access control solutions with advanced TCP/IP controllers, cloud integration, and high-performance multimodal biometric readers.


